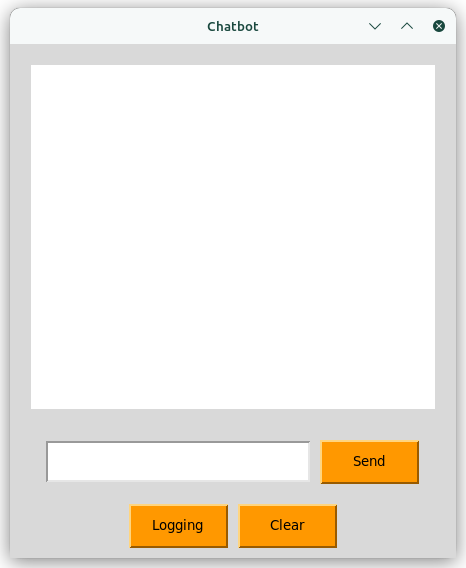
Hugging AI Chat Bot Alpha 001
Repo: https://github.com/AndreaKinder/HuChat-Chat-Bot-Assistant-Desktop/tree/master
Introduction
In today’s AI and natural language processing (NLP)-driven world, HuChat emerges as a user-friendly desktop application that facilitates seamless interaction with chatbots. Leveraging the power of the Hugging Face API, an open-source Python library for simplifying interactions with language models and chatbots, HuChat aims to provide an engaging and personalized assistant experience.
Technology Stack
Programming Language: Python
APIs and Dependencies:
- os
- json
- hugchat
- Tkinter
- Async
- Threading
User Interface Design:
UI Colors:
| Color Usage | Color Reference |
|---|---|
| Primary Color | d8d8d8 |
| Secondary Color (buttons, …) | fe9801 |
| Text Color | 000000 |
Alpha Version Functionality Overview
Primary Use Case
Desktop chatbot assistant.
Code
Code reference: https://github.com/AndreaKinder/HuChat-Chat-Bot-Assistant-Desktop/blob/master/src/main.py
Imports
- os: Provides tools for interacting with the operating system (creating folders, working with files).
- json: Handles JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) data, used to store login details.
- customtkinter as ctk: A library to make modern-looking interfaces with tkinter.
- hugchat: A library designed for interacting with a Hugging Face chatbot (which is likely a conversational AI model).
- hugchat.login: Provides functions to log into the Hugging Face chatbot service.
- tkinter as tk: The foundation of Python’s GUI toolkit.
- ttk: A tkinter extension for themed widgets (buttons, labels, etc.) that look nicer.
- asyncio: Enables asynchronous programming in Python, which helps manage tasks running concurrently.
- threading: Allows code to run in separate threads, preventing the main GUI from freezing.
Global Variables
- folder_name: The name of the folder where data will be saved (‘storage’).
- file_path: The complete path to the login information file (‘storage/log.json’).
- capture_id_chat: A list to keep track of chat conversation IDs.
- global_chatbot: Stores the main chatbot object that can be accessed from anywhere in the code.
Functions
- capture_log(us, passwd):
- Purpose: Stores the user’s username and password as a JSON file (‘log.json’).
- Creates the ‘storage’ folder if it’s missing.
- read_log():
- Purpose: Fetches the user’s username and password from ‘log.json’.
- check_directory(directory):
- Purpose: Checks to see if a folder exists.
- Example: if check_directory(‘storage’): print(‘The storage folder exists’)
- check_file_true():
- Purpose: A simple function to print a message indicating a directory and file were found.
- check_file_false():
- Purpose: Prints a message when a folder or file cannot be found. Also triggers the creation of the login window.
- check_file_log():
- Purpose: Looks for the login file (‘log.json’). If found, it allows automatic login. Otherwise, shows the login window.
- import_log():
- Purpose: Loads the user’s login information from ‘log.json’, if it exists.
- create_cookies():
- Purpose: Generates login cookies to use with the Hugging Face chatbot.
- How it works: It uses the import_log function to get login details and the Login object from the hugchat.login module.
- capture_id_chat_id(id_chat):
- Purpose: Stores chat conversation IDs to keep a history of conversations.
- create_chatbot():
- Purpose: Initializes the hugchat.ChatBot object. Also, it handles creating new chat instances when needed.
- chat_init(send): (Asynchronous)
- Purpose: Starts a chat and sends the user’s first message.
- How it works: It may create a new chat if none exist. Leverages the Hugging Face backend for the chatbot’s responses.
- chat_continue(send): (Asynchronous)
- Purpose: Continues a chat conversation that’s already in progress.
- chat_end():
- Purpose: Deletes all chats linked to the user’s login (this assumes the Hugging Face backend has the ability to do this).
- run_asyncio_coroutine(coroutine):
- Purpose: A helper to run an asynchronous coroutine (defined with async and await) within a thread. This is necessary for updating the GUI.
- send_question_async(question):
- Purpose: Asynchronously sends a question to the chatbot and updates the chat interface with the reply.
- How it works: Calls either chat_init or chat_continue, depending on whether there’s a chat in progress.
- clear_chat():
- Purpose: Deletes the chat history from the interface.
- send_question(event=None):
- Purpose: Gets the user’s text from the input box and starts the asynchronous sending process.
Classes
- InputUs(ctk.CTkFrame): A custom frame for entering the username.
- InputPasswd(ctk.CTkFrame): A custom frame for entering the password.
- ButtonLog(ctk.CTkButton): A custom button for logging in.
- App(ctk.CTk): The main window of the app; uses custom tkinter widgets for styling.